sessionmonitoring | Delinea | Bert Blevins | Session Monitoring
Enhancing Security with Session Monitoring in Privileged Access Management
YouTube
Just in Time Permissions Explained #Delinea #PAM #CyberSecurity
How Session Monitoring Elevates Privileged Access Management to Combat Insider Threats
1. Enhancing PAM with Session Monitoring: A Vital Security Layer
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is critical for controlling who can access sensitive systems, but session monitoring adds a vital layer by tracking exactly what privileged users do during their sessions. This continuous oversight helps detect unusual or risky behaviors in real time, reducing the window of opportunity for insider threats and external attackers.
2. How Session Monitoring Strengthens Privileged Access Security
Session monitoring complements PAM by providing detailed visibility into every action taken during privileged sessions. By recording keystrokes, commands, and application usage, organizations gain actionable insights that help identify unauthorized activities and swiftly mitigate potential breaches before damage occurs.
3. Detecting and Mitigating Risks with Session Monitoring
Risk detection is key to preventing security incidents involving privileged accounts. Session monitoring tools enable organizations to spot anomalies such as unexpected command executions or access to sensitive data, triggering automated alerts or session termination. This proactive approach helps contain threats and supports compliance requirements.
4. Why Session Monitoring is Essential for Effective PAM Deployment
While PAM controls access rights, session monitoring ensures accountability by continuously observing privileged user behavior. This combination not only enforces strict access policies but also provides forensic evidence that is critical during security audits or investigations, reinforcing trust in your cybersecurity framework.
5. Real-Time Risk Mitigation Through Session Monitoring
Session monitoring empowers security teams to intervene during high-risk activities by enabling real-time alerts and session shadowing. This capability allows rapid response to suspicious behavior, effectively mitigating risks before they escalate, and enhancing the overall security posture alongside PAM solutions.
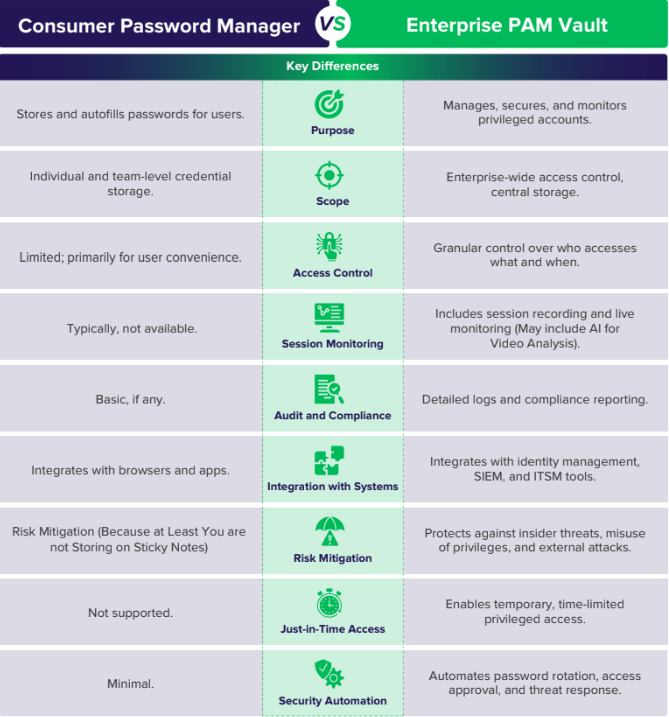
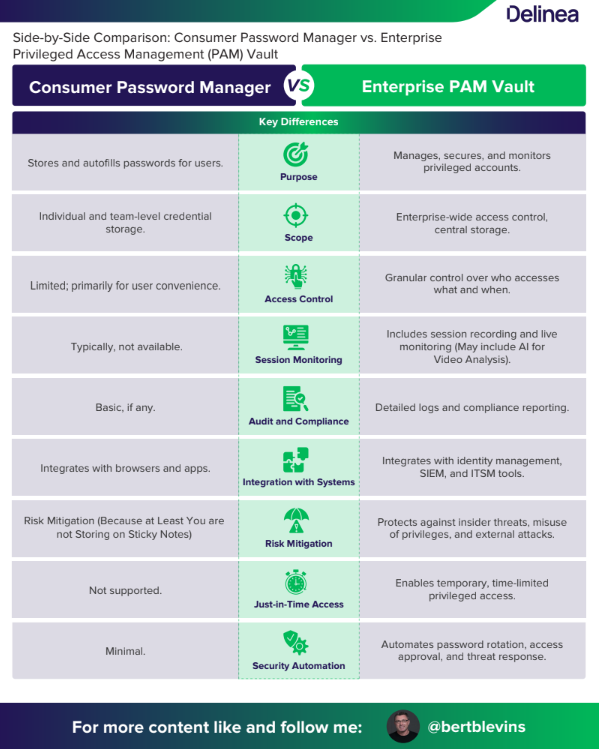
When to Use
For individual users or small teams managing personal or shared credentials.
When ease of use and convenience are top priorities.
For businesses without critical systems requiring strict access controls.
Use Cases
Individual Credential Management:
Employees managing their login details securely.
Shared Accounts:
Teams sharing credentials for tools like social media platforms.
Password Autofill:
Simplifying authentication for frequently accessed apps and
websites.
Other Considerations
Ease of Use:
Focus on user-friendly interfaces and browser integrations.
Cost:
Typically lower cost than PAM solutions.
Limited Security:
Does not address threats from privileged accounts or provide
session controls.

Securing Service Accounts with Delinea's Secret Server
How it works:
Secret Server discovers these accounts on Windows systems, manages their credentials, and rotates passwords automatically while updating dependent services to prevent disruptions.
How it works:
Integrates with AD to manage domain-level service accounts, rotating credentials and enforcing least privilege access across the domain.
How it works:
Identifies local accounts on individual machines, rotates their passwords, and ensures compliance with security policies.
How it works:
Manages accounts via SSH, rotating passwords and securing access to Unix/Linux systems hosting services or applications.
How it works:
Connects to database systems to rotate credentials and restrict access, ensuring secure database operations.
How it works:
Rotates credentials for IIS application pools and updates configurations to maintain uptime for web applications.
Cloud Service Accounts
How it works:
Integrates with cloud provider APIs (e.g.,
AWS IAM, Azure Entra ID, GCP) to
manage and rotate credentials for
cloud-based services.
Features used:
Cloud Discovery, API
Integration, Secret Vaulting.
Scheduled Task Accounts
How it works:
Manages accounts tied to Windows
Task Scheduler, rotating passwords and
updating task definitions seamlessly.
Features used:
Dependency Management,
RPC, Event Triggers.
Network Device Accounts
How it works:
Manages credentials for devices like
routers and switches via SSH or Telnet,
rotating passwords and securing access.
Features used:
Network Discovery, RPC,
Session Recording.
DevOps Service Accounts
How it works:
Secures accounts in CI/CD pipelines or
automation tools by vaulting credentials
and enabling secure API access.
Features used:
API Access, Secret Vaulting, Rotation Policies.
VMware ESX/ESXi Accounts
How it works:
Manages credentials for VMware
virtualization hosts, rotating passwords
and ensuring secure access to ESX/ESXi
systems.
Features used:
Discovery, RPC, Auditing.
Custom Service Accounts
How it works:
Allows tailored management for unique
applications or scripts, rotating
credentials and updating dependencies
as defined by custom scripts or
templates.
Features used:
Custom Templates, Scripting
(PowerShell/SSH),
Dependency Management.
The key to At Cyber Security
Privileged Account Management (PAM) – Planning and Preparation
Planning and Preparation
Implementing Privileged Access Management (PAM): Best Practices and Guidelines
Section 1: Best Practices for Onboarding Privileged Accounts
Section 2: Ensuring a Smooth Transition from Existing Processes to PAM
Section 3: Recommended Steps for Setting Up Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Effective Password and Credential Management in Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Password and Credential Management
What Policies Should We Implement for Password Rotation and Complexity in PAM?
How Can We Securely Manage Credentials for Non-Human Privileged Accounts, Such as APIs and Service Accounts?
Monitoring and Auditing
How Can Session Monitoring Be Used to Identify Anomalies?
Approaching Auditing for Compliance and Security
What Tools or Reports Can Simplify Audit Preparation?
Enforcing Least Privilege Principles with PAM
Balancing Security with Operational ESficiency
How Just-in-Time (JIT) Access Improves Security
Scenarios Suited for JIT:
How MFA Enhances PAM Security
Maintenance and Optimization
How often should PAM policies and configurations be reviewed and updated?
What steps can we take to continuously optimize PAM to adapt to evolving security needs?
How can AI or machine learning assist in identifying areas for improvement?
Training and User Adoption for PAM (Privileged Access Management) Tools
What training formats (e.g., hands-on, virtual, or documentation) are most effective?
What strategies can we use to gain user adoption and avoid resistance when implementing PAM?
How can we communicate the importance of PAM without overwhelming users?
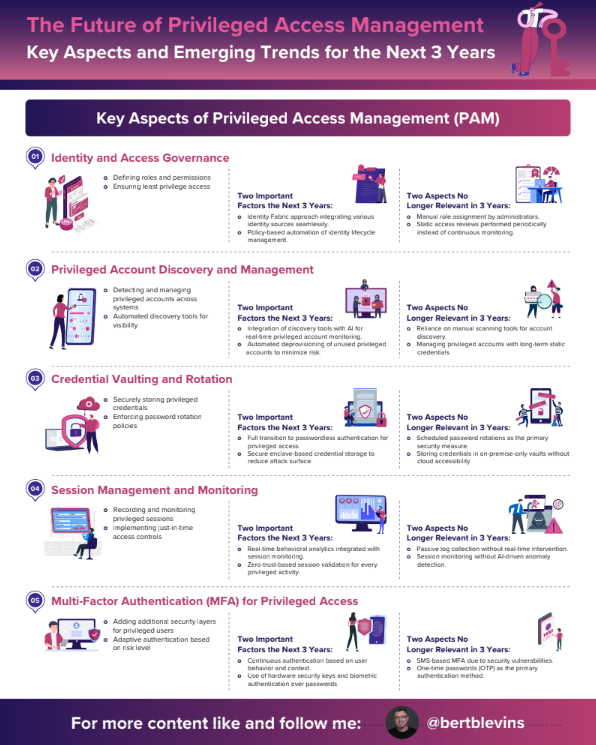
Key Aspects of Privileged Access Management (PAM)
- Identity and Access Governance: Defining roles and permissions
- Privileged Account Discovery and Management: Detecting and managing privileged accounts across systems
- Credential Vaulting and Rotation: Securely storing privileged credentials
- Session Management and Monitoring: Recording and monitoring privileged sessions
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for Privileged Access: Adding additional security layers for privileged users
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Access Management: Granting temporary privileged access as needed
- Privileged Access Risk Analytics: Using AI/ML for behavior-based risk assessment
- Cloud and Hybrid PAM Integration: Extending PAM capabilities to multi-cloud environments
- Third-Party and Remote Access Management: Securing vendor and contractor access
- Compliance and Audit Reporting: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations
Real-time Threat Detection
Real-time visibility into the actions of privileged users is possible through session monitoring. It enables security teams to quickly identify suspicious activity, including attempts at illegal access, strange commands, and data exfiltration.
Compliance Requirements
Strict controls over privileged access are required by numerous regulatory standards, including GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Additionally, these standards require organizations to monitor and audit such activities. By ensuring adherence to these rules, session monitoring protects enterprises from costly fines and penalties.
Insider Threat Mitigation
Insider threats represent a serious risk to enterprises, regardless of their motivation. Monitoring privileged sessions helps avoid potential data breaches and sabotage by identifying unusual activity by trusted insiders early on.
Forensic Analysis
Detailed session logs can be an invaluable piece of forensic evidence in the sad event of a security incident. These logs can be examined by security teams to determine the extent of the breach, pinpoint its primary source, and implement the required corrective measures.
Implementing Effective Session Monitoring
Think of recording complete privileged sessions for playback and review in addition to logging. Recordings from sessions offer a thorough audit trail of user actions and make in-depth research easier when looking into security incidents.

Challenges and Considerations

Privacy Concerns
It's critical to strike a balance between user privacy rights and the necessity of session tracking. In order to ensure compliance with pertinent privacy rules, organizations must develop explicit policies governing the collection, storage, and use of session data.
Performance Impact
Systems and networks may have overhead from session monitoring, especially in settings where there is a lot of activity from privileged users. To reduce any bottlenecks, organizations should thoroughly assess the performance impact and put scalable solutions in place.
Integration Complexity
It can be difficult to integrate session monitoring features with the IT architecture and current PAM systems. In order to guarantee a smooth integration and little interruption to operations, meticulous planning, coordinating, and testing are necessary.
User Awareness and Training
It is essential to inform privileged users about the intent behind and potential consequences of session monitoring. A culture of responsibility and openness can be promoted and worries can be allayed with the aid of training programs and clear communication.
YouTube
OATH OTP MFA Explained: Easy Setup Guide for Stronger Security

Enhancing Security Posture
Swift Response to Anomalies
Swift Response to Anomalies
Compliance and Auditing
Enhancing Security Posture
The Importance of Session Monitoring for Remote Access to Critical Systems

Best Practices for Session Monitoring
Implement Robust Authentication
Utilize strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to prevent unauthorized access to remote systems.
Encrypt Session Traffic
Encrypt remote sessions using secure protocols like SSL/TLS to protect data in transit from eavesdropping and tampering.
Role-based Access Control
Enforce role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict privileges based on user roles and responsibilities, minimizing the risk of privilege abuse.
Continuous Monitoring
Continuously monitor remote sessions for suspicious activities, leveraging automated tools to detect anomalies and unauthorized actions.
Regular Auditing and Review
Conduct regular audits of session logs and review monitoring reports to identify security gaps, improve policies, and enhance overall security posture.
In this day and age, where remote access is common, protecting vital systems must come first. With its ability to provide real-time visibility, anomaly detection, and forensic capabilities to efficiently reduce security threats, session monitoring becomes an essential part of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Establishing best practices for session monitoring and utilizing sophisticated monitoring technologies can help businesses become better at identifying and addressing risks, protecting their vital systems from possible assaults.